Tag: Peilong Lu
-

Congrats Green!
Postdoc Green Ahn, PhD, has been named a 2024 Jane Coffin Childs-HHMI Fellow. She’s probing biology in new ways to build tomorrow’s cancer treatments.
-

Congrats Ljubica!
With support form the Helen Hay Whitney Foundation, postdoc Lj Mihaljevic, PhD, is building membrane proteins with advanced functions from the ground up.
-
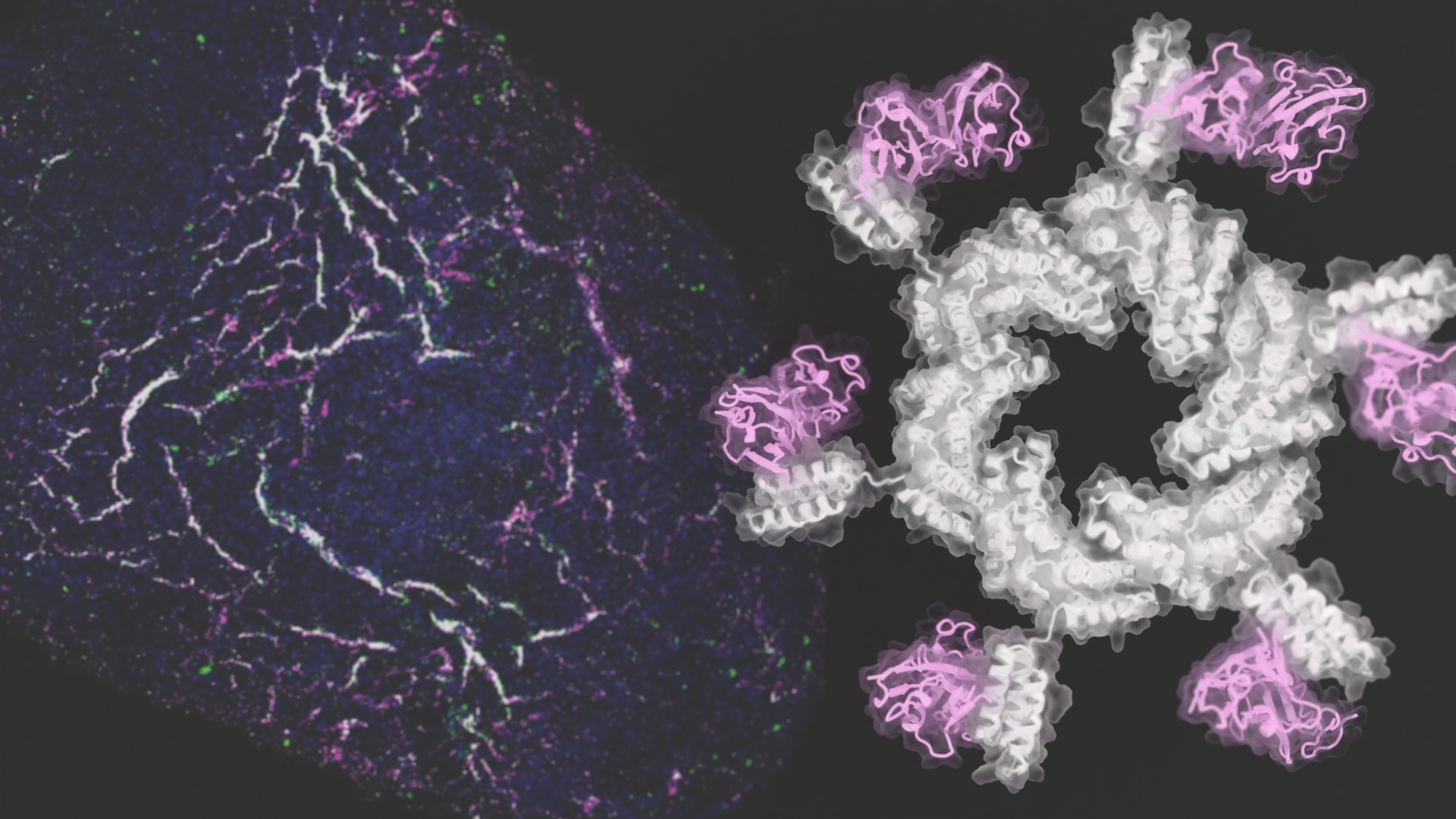
Designed proteins guide stem cells to form blood vessels
Today we report in Cell on the de novo design of proteins that direct human stem cells to form new blood vessels in the lab. This newfound control over stem cell development is a step toward more effective regenerative medicines. “Whether through heart attack, diabetes, and the natural process of aging, we all accumulate damage…
-

Congrats Xinru!
Postdoctoral scholar Xinru Wang, PhD, has been named a 2024 Leading Edge Fellow. She’s designing drugs that activate rather than inhibit their targets.
-
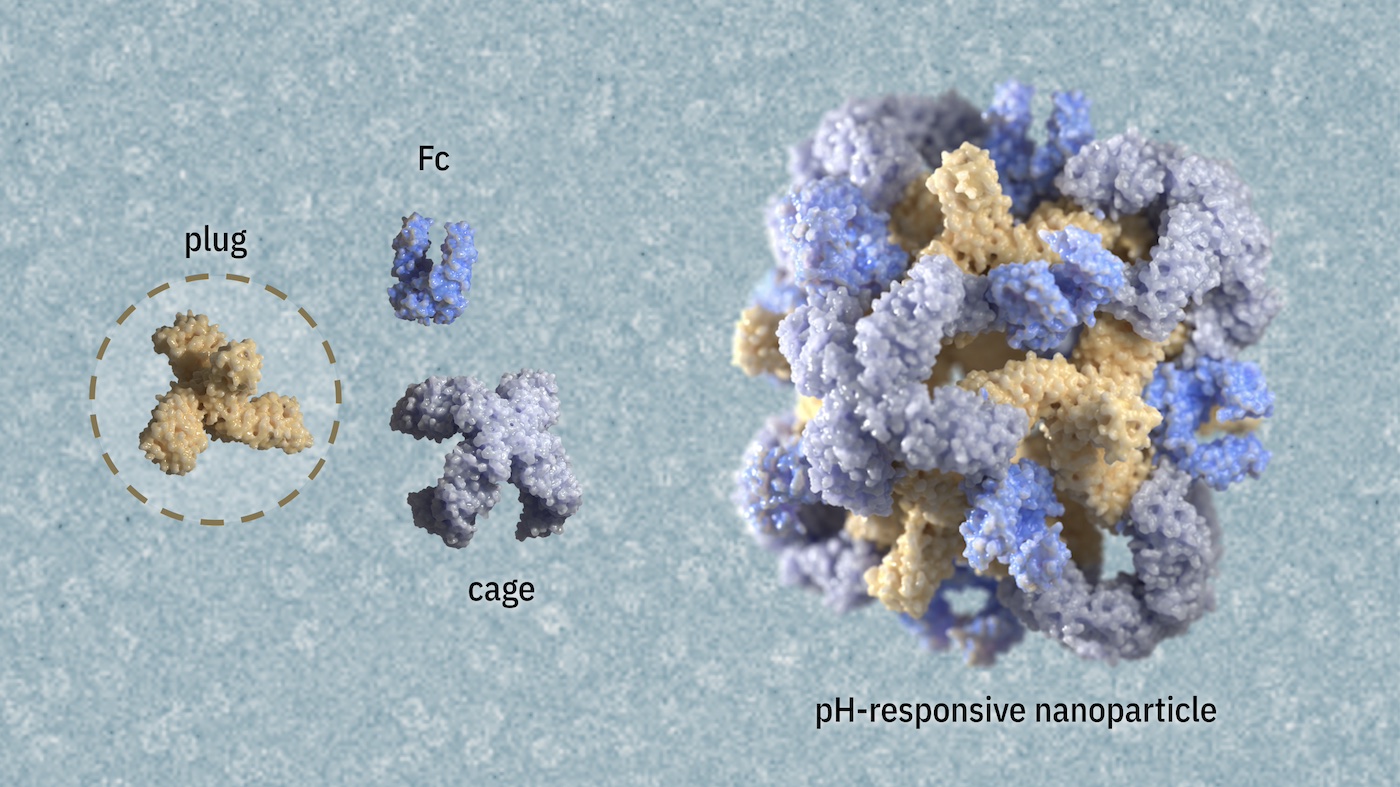
pH-responsive nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery
This novel technology may reduce side effects and enhance treatment outcomes for a wide range of diseases.
-
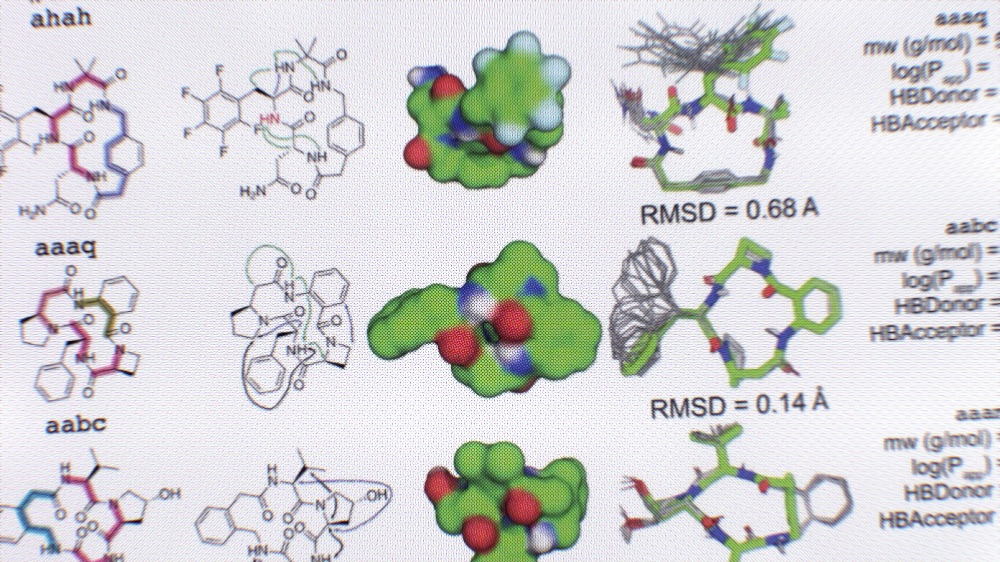
Expansive discovery of diverse macrocycles
In a new study in Science, we introduce an AI-assisted drug discovery approach and use it to generate over 14.9 million never-before-seen peptides with appealing pharmaceutical features, including molecules that inhibit key proteins linked to coronavirus infection and cancer in the lab. This research was led by Patrick Salveson, a recent postdoc in the lab.…
-
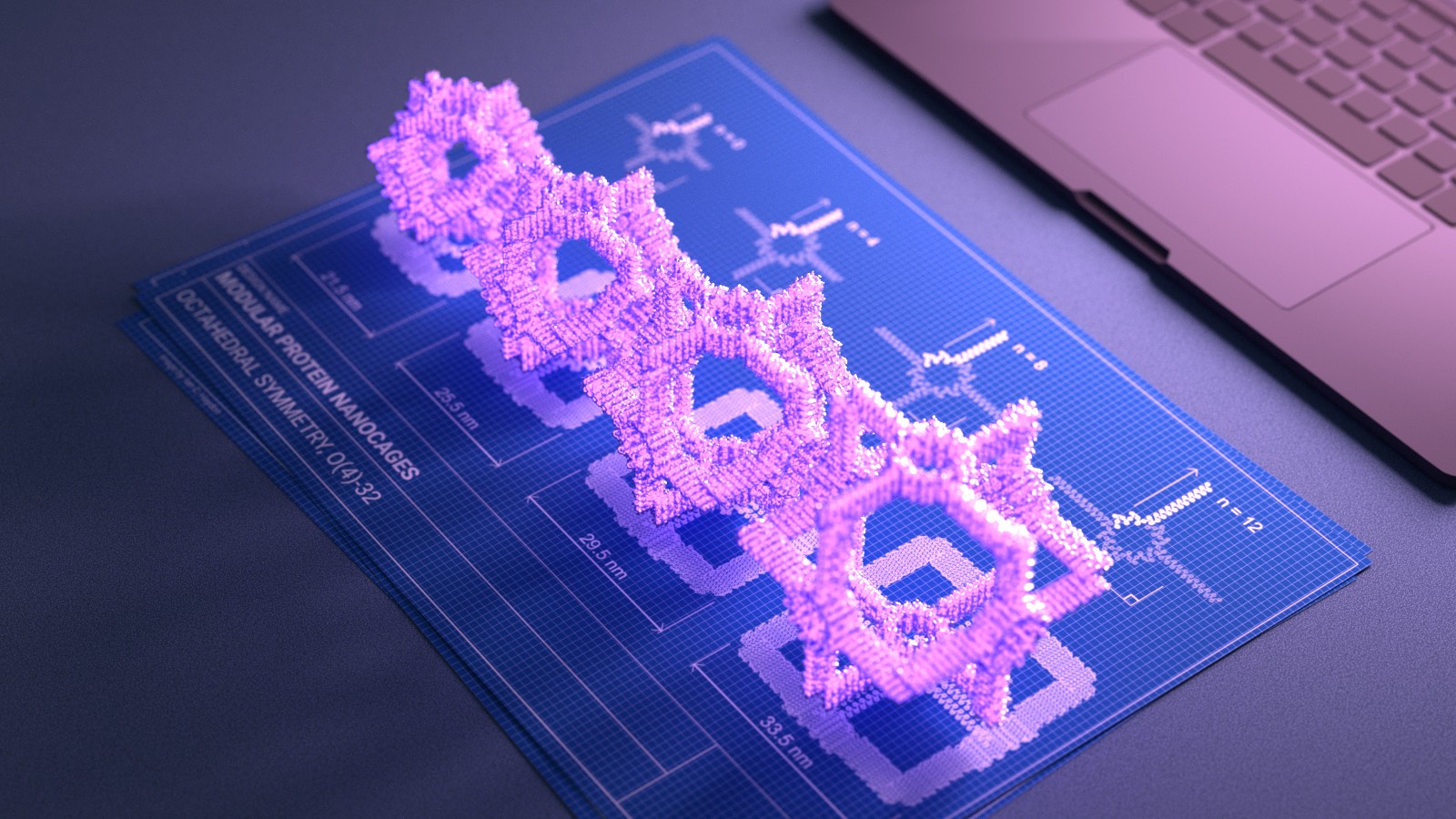
Simplifying nanoscale design with regular protein building blocks
Consistent protein parts allow builders to create biomaterials according to their needs.
-
Modeling and generating more of life’s building blocks
All-atom versions of the modeling tool RoseTTAFold and the design tool RFdiffusion are now freely accessible to the scientific community.