-
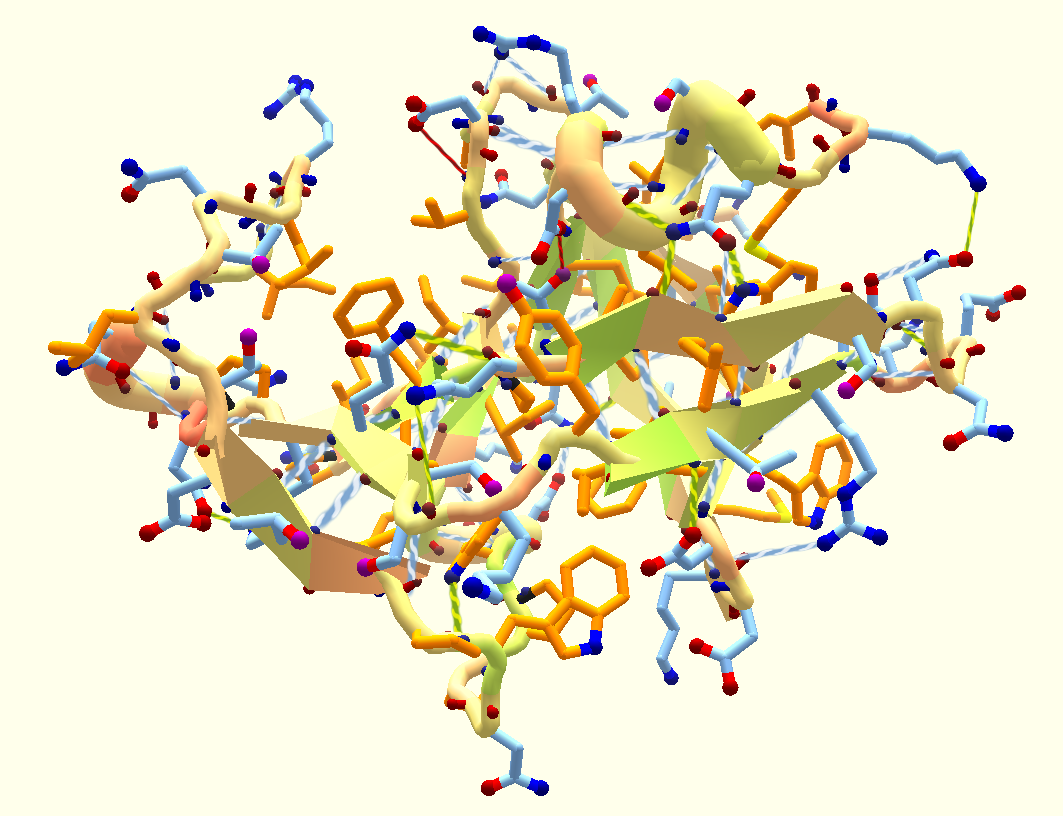
Crystal structure of a monomeric retroviral protease solved by protein folding game players
Khatib, F., DiMaio F., Contenders Group F., Void Crushers Group F. et al. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2011) Following the failure of a wide range of attempts to solve the crystal structure of the Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (M-PMV) retroviral protease by molecular replacement, we challenged players of the protein folding game Foldit to produce…
-
Computational design of protein inhibitors of Spanish and avian flu hemagglutinin
Fleishman, S. J., Whitehead T. A., et al. Science 332, 816-821. (2011) We developed a new computational method for designing protein interactions and applied it to the design of anti-flu hemagglutinin inhibitors. The proteins were designed using computational resources generously provided by Rosetta @ Home participants and inhibited the function of the hemagglutinin flu coat…
-
Improved molecular replacement by density- and energy-guided protein structure optimization
DiMaio, F., Terwilliger T. C et al. Nature (2011) We show that the crystallographic phase problem can be solved using distant evolutionary relationships by combining algorithms for protein structure modelling with those developed for crystallographic structure determination. Ingegrating Rosetta structure modelling with Autobuild chain tracing yielded high-resolution structures for 8 of 13 X-ray diffraction data…
-
Determining large protein structures (>200 amino acids) from limited NMR data using Rosetta
Raman, Lange et al, Science, 327, 1014-8. (2010) Large protein structures can now be determined by incorporating backbone-only NMR data into Rosetta. Shown here is the structural comparison of ALG13 (201 amino acids) determined.(A) computationally using RDCs and backbone NH-NH NOEs. (B) experimentally by conventional NMR methods (PDB id : 2jzc) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is…
-
Computational design and optimization of Kemp eliminases
Rothlisberger D., Khersonsky O. et al, Nature, 453, 164-6. (2008) Khersonsky O., Rothlisberger D. et al, J Mol Biol, 396(4), 1025-42. (2010) We designed several enzymes that catalyze Kemp elimination, a model reaction for proton transfer from carbon. These enzymes utilize two catalytic motifs and enhance the reaction rate up to 105-fold with multiple turnovers. …
-
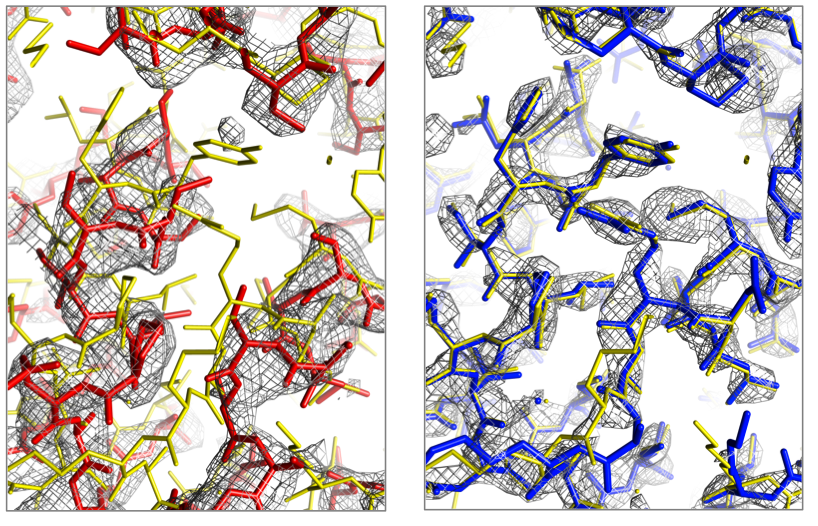
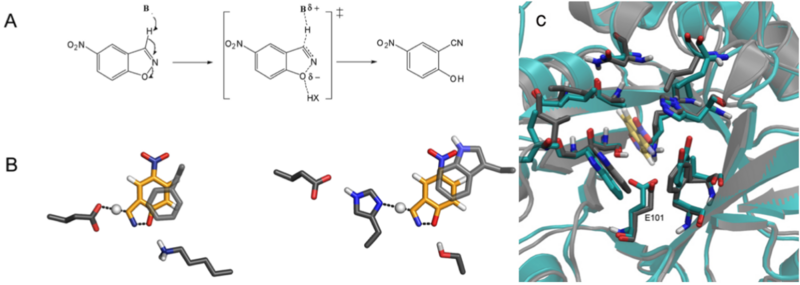
Computational design of an enzyme catalyst for a stereoselective bimolecular Diels-Alder reaction
Siegel and Zanghellini et al, Science, 329, 309-313. (2010) Structure of a designed Diels-Alderase. (A) Surface view of the design model (DA_20_00, green) bound to the substrates (diene and dienophile, purple). The catalytic residues making the designed hydrogen bonds are depicted as sticks. (B) Overlay of the design model (DA_20_00,brown) and crystal structure of DA_20_00_A74I (green). The crystal…
-
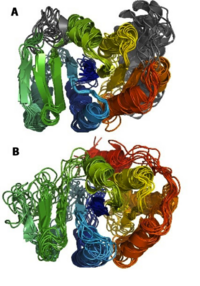
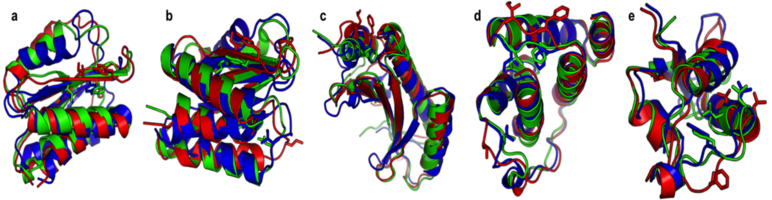
Structure prediction problems solved by Foldit players
Cooper, Khatib et al, Nature, 466, 756-60. (2010) Examples of blind structure prediction problems in which players were successfully able to improve structures. Native structures are shown in blue, starting puzzles in red, and top scoring Foldit predictions in green. (a) The red starting puzzle had a register shift and the top scoring green Foldit prediction…
-
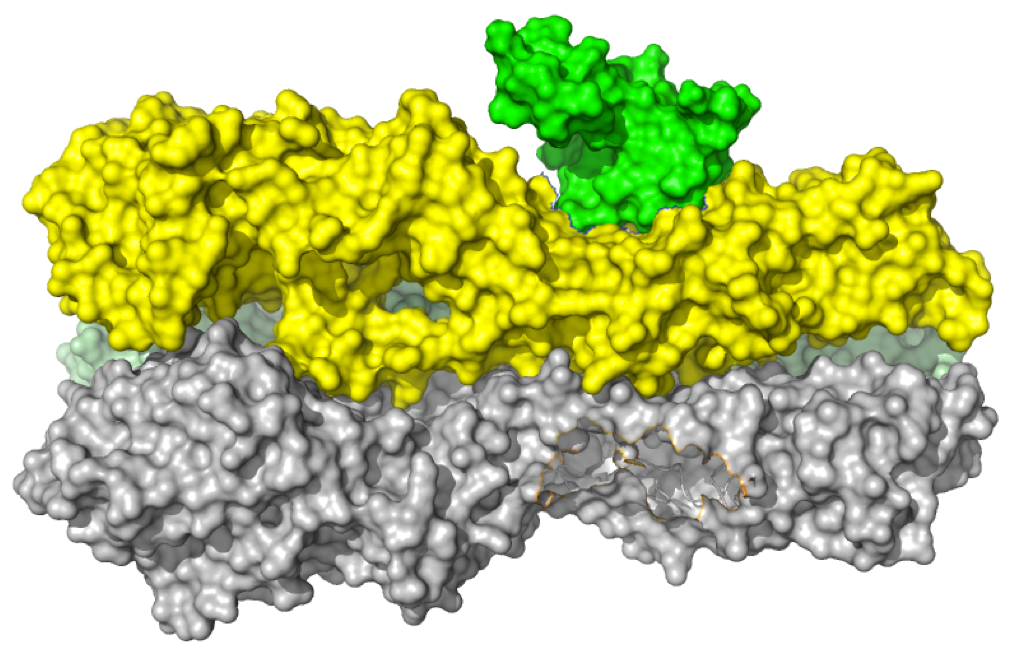
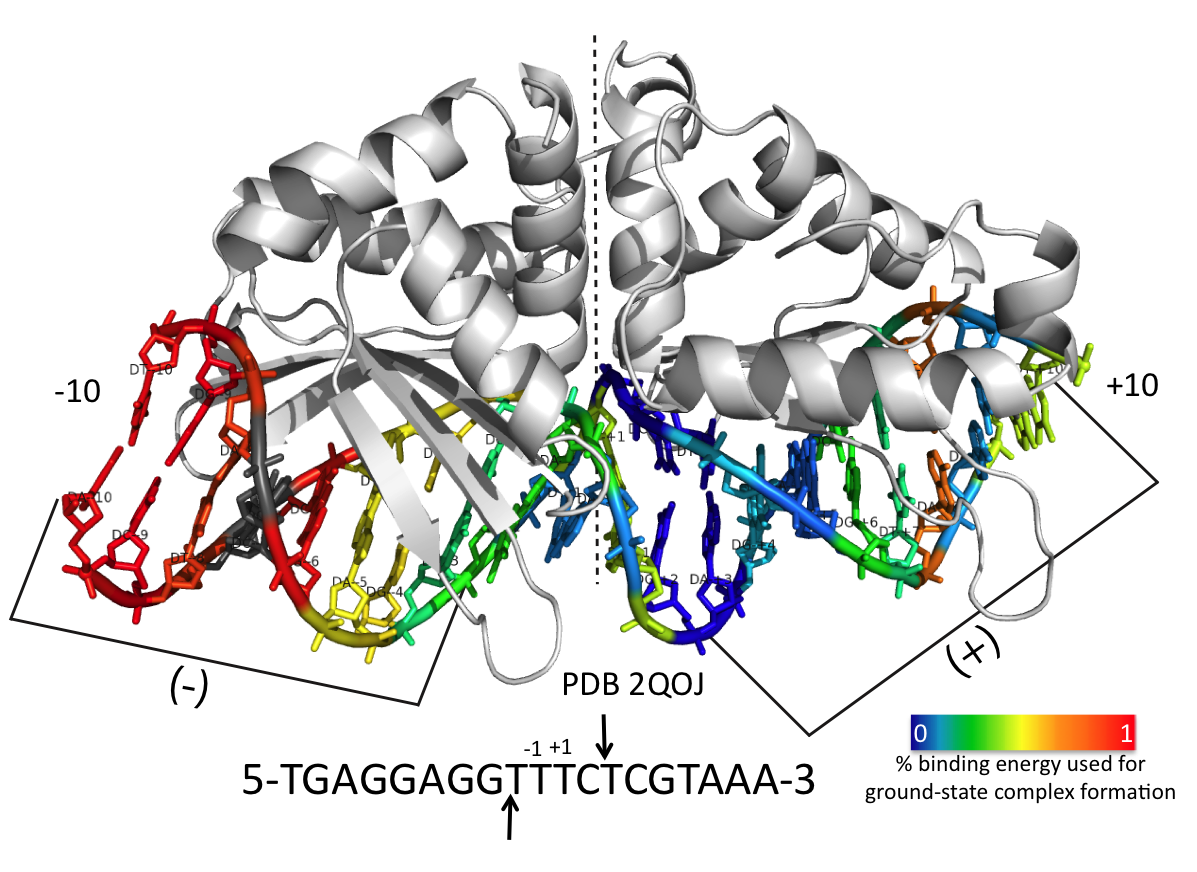
Exploitation of binding energy for catalysis and design
Thyme, Summer B., et all. Nature 461, 1300-4. (2009) The monomeric homing endonuclease I-AniI cleaves with high sequence specificity in the center of a 20 base-pair DNA target site, with the N-terminal domain of the enzyme making extensive binding interactions with the left (-) side of the target site and the similarly structured C-terminal domain…