-
RFdiffusion now free and open source
Today we are making RFdiffusion, our artificial intelligence (AI) program that can generate novel proteins with potential applications in medicine, vaccines, and advanced materials, free for both non-profit and for-profit use under a governed license. The software, which has been tested in the lab, is much faster and more capable than prior protein design tools.…
-
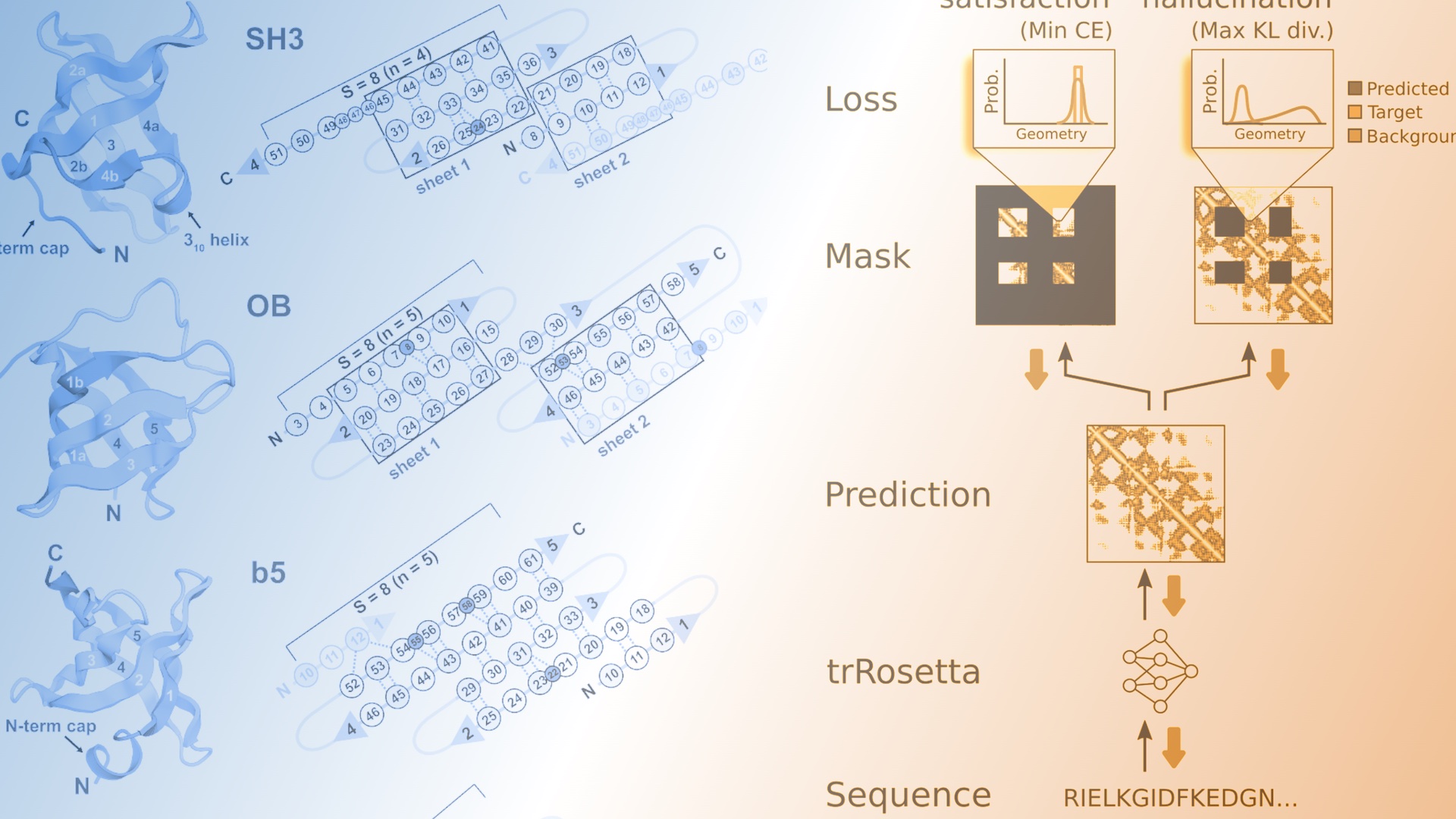
De novo design of small beta barrel proteins
The de novo design of small proteins with beta-barrel topologies has been a challenge for computational design due to the complexity inherent in these folds. In a new study appearing in PNAS, a team led by Baker Lab research scientist David E. Kim describes the successful design and characterization of four different classes of small…
-
Machine learning generates custom enzymes
Today we report in Nature [PDF] the computational design of highly efficient enzymes unlike any found in nature. Laboratory testing confirms that the new light-emitting enzymes, called luciferases, can recognize specific chemical substrates and catalyze the emission of photons very efficiently. This is an important step in the field of protein design as enzymes have many uses…
-
NBC: “Scientists use new A.I. tech to fight diseases”
NBC News Now recently covered how we are using artificial intelligence to accelerate protein science. From NBC News Now A group of researchers at the University of Washington is harnessing artificial intelligence to improve how scientists develop proteins for medicines and vaccines. NBC’s Dr. Akshay Syal has a closer look at the potential medical breakthrough.
-
New York Times: “A.I. Turns Its Artistry to Creating New Human Proteins”
The New York Times recently wrote about one of our latest preprints. In it, we introduce a generative diffusion model for protein design called RFdiffusion. [Update: This research was subsequently published in Nature, and RFdiffusion is now free and open source.] From the New York Times: Last spring, an artificial intelligence lab called OpenAI unveiled…
-
To improve a cytokine mimic, cut it in half
This week we reported in Nature Biotechnology the design of a conditionally active mimetic of IL-2 that reduces the toxicity of systemic cytokine therapy. This work builds on our prior efforts to create functional interleukin mimics with reduced toxicity. We first described Neoleukin-2/15 (Neo-2/15) in 2019. This compact protein reproduces the immunostimulatory function of IL-2…
-
ProteinMPNN excels at creating new proteins
Over the past two years, machine learning has revolutionized protein structure prediction. Now, three papers in Science describe a similar revolution in protein design. In the new papers, we show that machine learning can be used to create proteins much more accurately and quickly than previously possible. This could lead to many new vaccines, treatments,…
-
Design of permeable peptides leads to new spinout (Vilya)
Researchers at the Institute for Protein Design have discovered how to create peptides that slip through membranes and enter cells. This drug design breakthrough may lead to new medications for a wide variety of health disorders, including cancer, infection, and inflammation. This research appears in the journal Cell [PDF]. Gaurav Bhardwaj, Adam Moyer, Naozumi Hiranuma,…