Category: Uncategorized
-
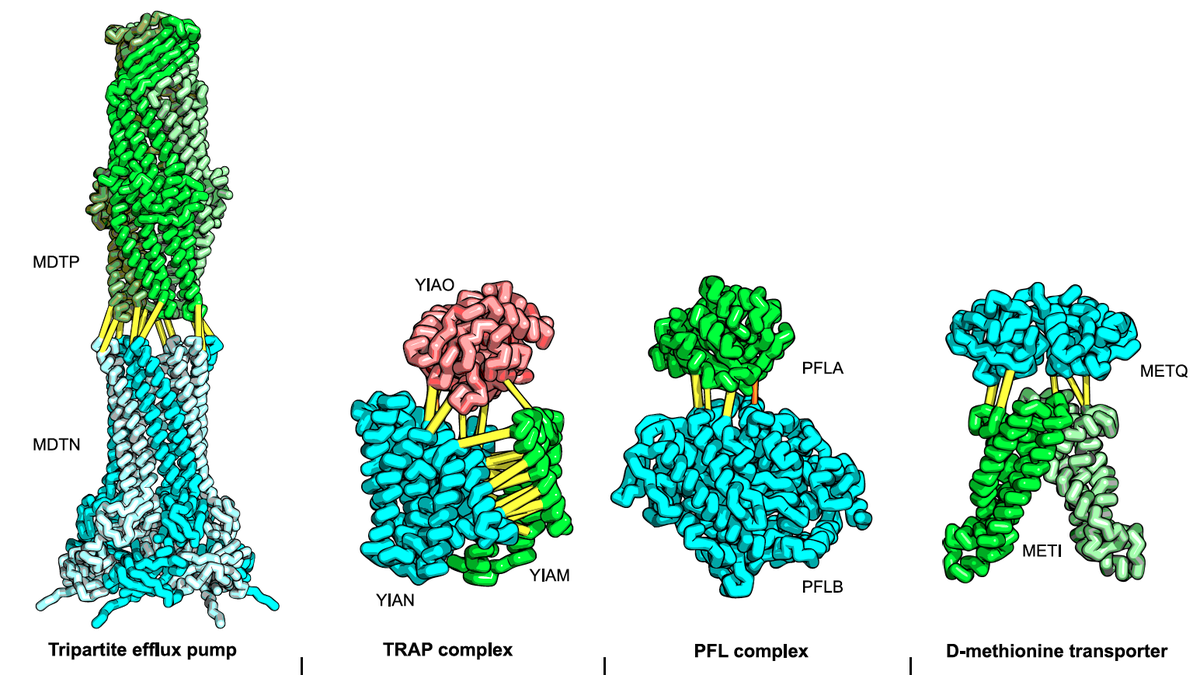
Robust and accurate prediction of residue-residue interactions across protein interfaces using evolutionary information
Do the amino acid sequence identities of residues that make contact across protein interfaces covary during evolution? If so, such covariance could be used to predict contacts across interfaces and assemble models of biological complexes. We find that residue pairs identified using a pseudo-likelihood-based method to covary across protein–protein interfaces in the 50S ribosomal unit…
-
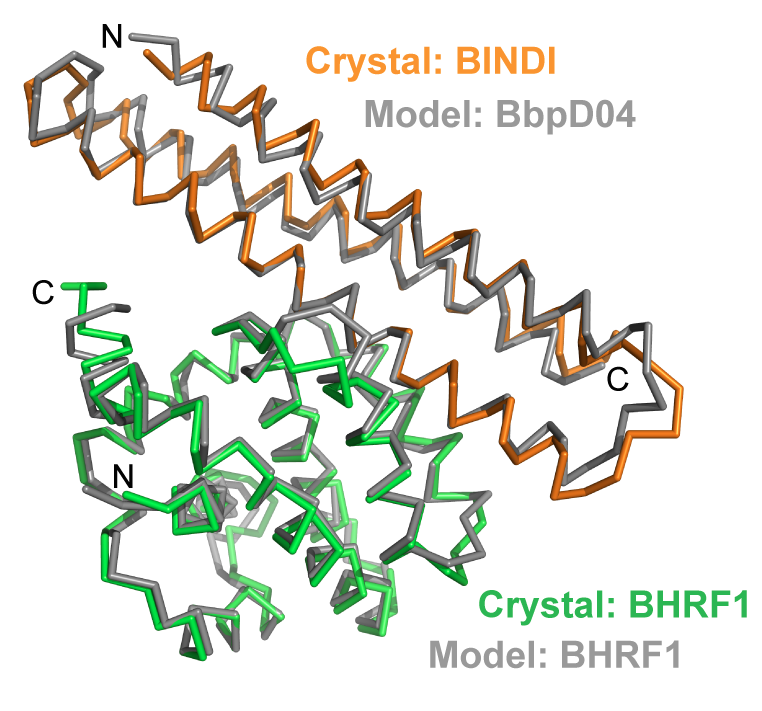
A computationally designed inhibitor of an Epstein-Barr viral Bcl-2 protein induces apoptosis in infected cells
Since apopotosis of infected cells can limit virus production and spread, some viruses have co-opted prosurvival genes from the host. This includes the Epstein-Barr virus gene BHRF1, a homologue of human Bcl-2 proteins that block apoptosis and are associated with cancer. Here we describe an approach where computational design and experimental optimization were used to…
-
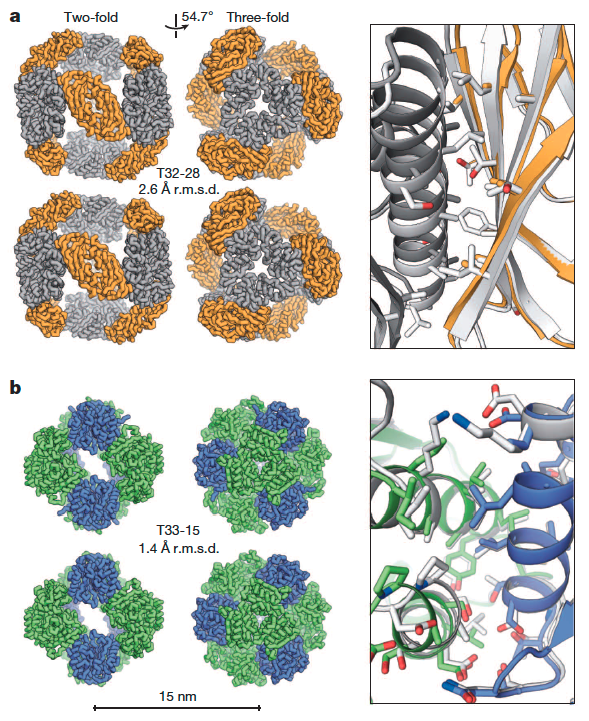
Accurate design of co-assembling multi-component protein nanomaterials
The self-assembly of proteins into highly ordered nanoscale architectures is a hallmark of biological systems. The sophisticated functions of these molecular machines have inspired the development of methods to engineer self-assembling protein nanostructures; however, the design of multi-component protein nanomaterials with high accuracy remains an outstanding challenge. Here we report a computational method for designing protein nanomaterials in which multiple copies of two distinct subunits co-assemble…
-
Removing T-cell epitopes with computational protein design
King, C. et al. PNAS 111, 8577-82 (2014) Immune reposes can make protein therapeutics ineffective or even dangerous. Here we describe a general computational protein design method for reducing immunogenicity by eliminating known and predicted T-cell epitopes and maximizing the content of human peptide sequences without disrupting protein structure and function. We show that the method…
-
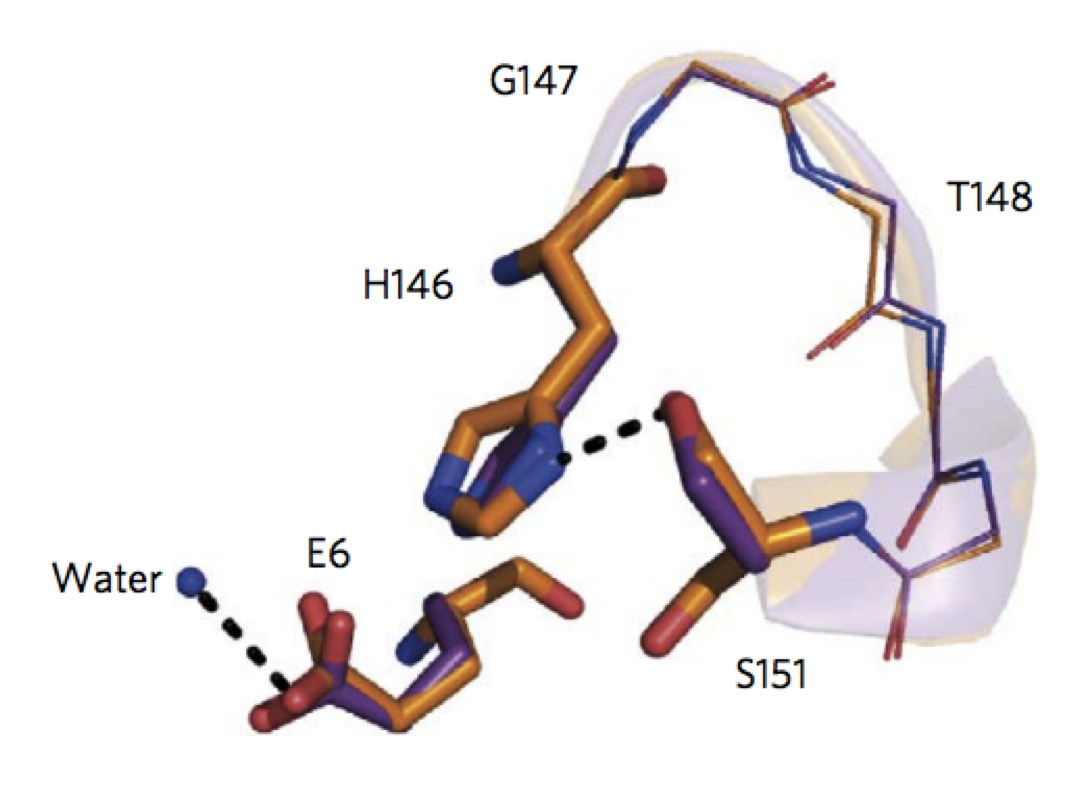
Design of activated serine-containing catalytic triads with atomic-level accuracy
Rajagopalan, S., Wang, C., et al. Nat Chem Bio. 10(5), 386-391 (2014) A challenge in the computational design of enzymes is that multiple properties, including substrate binding, transition state stabilization and product release, must be simultaneously optimized, and this has limited the absolute activity of successful designs. Here, we focus on a single critical property…
-
Proof of principle for epitope-focused vaccine design
Correia, B.E. et al. Nature 507, 201-6 (2014) Vaccines prevent infectious disease largely by inducing protective neutralizing antibodies against vulnerable epitopes. Several major pathogens have resisted traditional vaccine development, although vulnerable epitopes targeted by neutralizing antibodies have been identified for several such cases. Hence, new vaccine design methods to induce epitope-specific neutralizing antibodies are needed.…
-
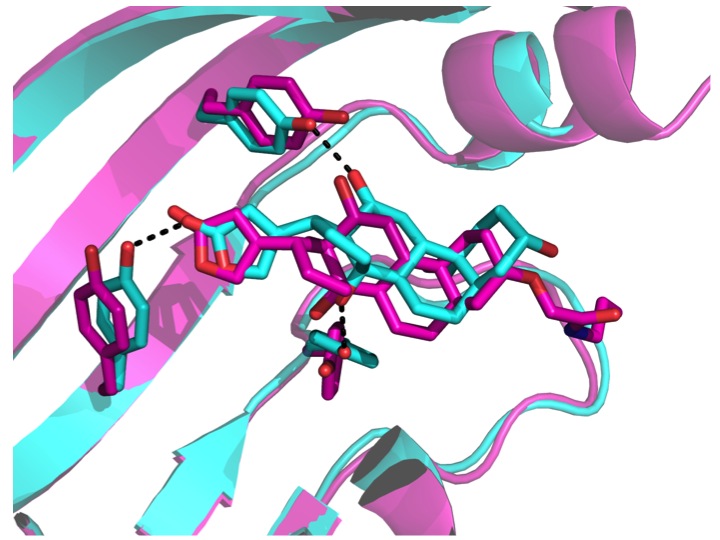
Computational design of ligand-binding proteins with high affinity and selectivity
Tinberg, C.E., Khare, S.D., et al. Nature. 501(7466), 212-216. (2013) We describe a computational approach for designing proteins that bind small molecules and use it to create binders for digoxin, a steroid toxin deriving from the foxglove plant. The method relies on the explicit design of highly energetically favorable interactions with the ligand. Directed laboratory evolution…
-
Computational design of an α-gliadin peptidase
Gordon, S.R., Stanley, E.J., et al. J Am Chem Soc. 134(50), 20513-20520. (2012) The ability to rationally modify enzymes to perform novel chemical transformations is essential for the rapid production of next-generation protein therapeutics. Here we describe the use of chemical principles to identify a naturally occurring acid-active peptidase, and the subsequent use of computational…